Table of Contents
9. Table meshDebug¶
The table meshDebug is used to build, debug and save to binary file any format supported by the engine.
The idea of this object, is to construct any object available in the engine or import an object from the well know Wavefront for example.
The table meshDebug is not a renderizable object, than, there is no common methods inherited.
The table meshDebug support the following types from engine:
Types
Expected file extension
mesh
mshsprite
sptfont
fnttexture
pngjpegetcshape
-particle
ptltile
tile
9.1. Primitive options¶
9.1.1. mode draw¶
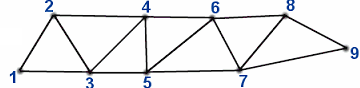
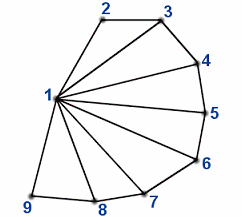
The mode draw is the way to specific triangle primitives.It is based on different interpretations of the vertex stream.Next the table explaining the interpretation of each of them:
Mode
Explanation
TRIANGLES
TRIANGLE_STRIP
TRIANGLE_FAN
LINES
LINE_LOOP
LINE_STRIP
POINTS
Important
TRIANGLES.9.1.2. cull face¶
Triangle primitives after all transformation steps have a particular facing.This is defined by the order of the three vertices that make up the triangle, as well as their apparent order on-screen.Triangles can be discarded based on their apparent facing, a process known as face culling.Next the table the engine option:
Types
Comment
FRONT
BACK
Default for the engine.
FRONT_AND_BACK
Will draw both sides.
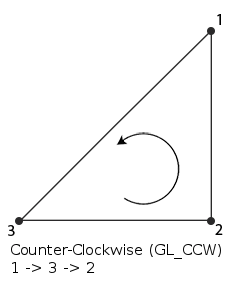
9.1.3. front face direction¶
Triangle primitives are drawing following the direction clockwise or counter-clockwise.The table shows the directions:
Types
Comment
CW
Default for the engine.
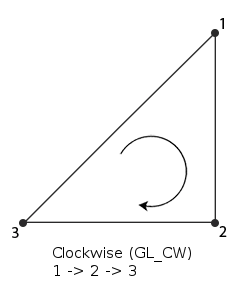
CCW
9.2. static methods¶
9.2.1. meshDebug getInfo¶
- getInfo(string file_name)¶
- Parameters
string – file_name to be save.
- Returns
table- result.
Example:
local infoTable = meshDebug:getInfo('crate.msh')
if infoTable then
print('info','The table has the following information:')
for k, v in pairs(infoTable) do
if type(v) == 'table' then
for k2, v2 in pairs(v) do
print(k, k2, v2)
end
else
print( k, v)
end
end
end
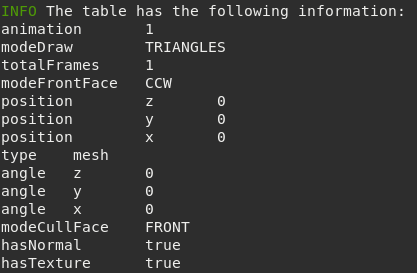
Figure 9.1 Possible output.¶
Note
9.2.2. meshDebug getType¶
- getType(string file_name)¶
- Parameters
string – file_name of mesh.
- Returns
string- will be one of option from table type of mesh.
Example:
local type = meshDebug:getType('crate.msh')
print('info','type of crate.msh',type)
--possible output:
--type of crate.msh mesh
Note
9.2.3. meshDebug getExt¶
- getExt(string file_name)¶
Given an string it will return the extension. Will look for the last
.in the string and return the string after that.- Parameters
string – file_name of mesh.
- Returns
string- extension.
Example:
local ext = meshDebug:getType('crate.msh')
print('expected msh:',ext)
--output:
--expected msh:msh
Note
9.3. meshDebug methods¶
9.3.1. meshDebug new¶
tMyMesh = meshDebug:new()
9.3.2. meshDebug load¶
- load(string file_name)¶
- Parameters
string – file_name to be loaded.
- Returns
boolean- result.
Example:
tMyMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMyMesh:load("particle.ptl") then
print("Success ...")
else
print("Failed to load mesh...")
end
Note
- load(renderizable mesh)¶
- Parameters
renderizable – mesh to be loaded from memory.
- Returns
boolean- result.
Example:
tMyMesh = meshDebug:new()
tSprite = sprite:new()
if tSprite:load('mike.spt') then
if tMyMesh:load(tSprite) then
print("Success loaded sprite from memory...")
else
print("Failed to load mesh...")
end
else
print("Failed to load sprite...")
end
Important
The USE_EDITOR_FEATURES flag must be enabled to this method work.
9.3.3. meshDebug save¶
- save(string file_name)¶
- Parameters
string – file_name to be save.
- Returns
boolean- result.
Example:
tMyMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMyMesh:load("mario.spt") then
--do something (modify vertex etc)
if tMyMesh:save("mario2.spt") then
print("Success ...")
else
print("Failed to save file")
end
else
print("Failed to load mesh...")
end
Note
The types are described at this table.
9.3.4. meshDebug setType¶
- setType(string new_type)¶
Modify or set the internal type of mesh.
- Parameters
string – could be one of option from table type of mesh.
- Returns
boolean- result.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('crate.msh') then
print('my type:', tMesh:getType())
tMesh:setType('sprite')
print('my new type:', tMesh:getType())
end
Note
9.3.5. meshDebug animation¶
- addAnim(string name, number initialFrame, number finalFrame, number timeBetweenFrame, number typeAnimation)¶
Add a new animation.
- Parameters
string – name of animation (new).
number – index initial frame one based.
number – index final frame one based.
number – time between frames.
number – type animation (see type of animation).
- Returns
number- Index animation added one based.
See animation animation for more detail.
Example getting an animation:
tMyMeshDebug = meshDebug:new()
if tMyMeshDebug:load('crate.msh') then
local animation_name = 'default'
local initialFrame = 1
local finalFrame = 10
local timeBetweenFrame = 0.3
local typeAnimation = mbm.GROWING_LOOP
local index = tMyMeshDebug:addAnim(animation_name,initialFrame,finalFrame,timeBetweenFrame,typeAnimation)
print('animation added number:',index)
end
Note
- getAnim(number index_animation)¶
Get detail of animation.
- Parameters
number – index_animation from 1 to max number of animation.
- Returns
string,number,number,number,number- Animation name,initial frame,final frame, time between frame, type of animation.
See animation animation for more detail.
Example getting an animation:
tMyMeshDebug = meshDebug:new()
if tMyMeshDebug:load('crate.msh') then
local animation,initialFrame,finalFrame, timeBetweenFrame, typeAnimation = tMyMeshDebug:getAnim(1)
print('animation :',animation)
print('initialFrame :',initialFrame)
print('finalFrame :',finalFrame)
print('timeBetweenFrame:',timeBetweenFrame)
print('typeAnimation :',typeAnimation)
end
Note
Note that this method differs from getAnim inherited from renderizable because it is not a renderizable.
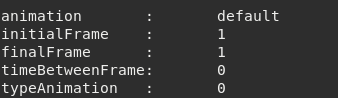
Figure 9.2 Possible output.¶
Note
Note that this method differs from getAnim inherited from renderizable because it is not a renderizable.
- updateAnim(number index, string name, number initialFrame, number finalFrame, number timeBetweenFrame, number typeAnimation)¶
Update an existent animation.
- Parameters
number – index animation one based.
string – name of animation (new).
number – index initial frame one based.
number – index final frame one based.
number – time between frames.
number – type animation (see type of animation).
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
tMesh:updateAnim(1,'stand',1,5,0.33,mbm.GROWING_LOOP)
end
- copyAnimationsFromMesh(table renderizable)¶
Example:
tMesh = mesh:new()
if tMesh:load('crate.msh') then
tMyMeshDebug = meshDebug:new()
local animation,initialFrame,finalFrame, timeBetweenFrame, typeAnimation = tMyMeshDebug:getAnim(1)
print('Before copy animation from crate.msh, animation :',animation)
print('Before copy animation from crate.msh, initialFrame :',initialFrame)
print('Before copy animation from crate.msh, finalFrame :',finalFrame)
print('Before copy animation from crate.msh, timeBetweenFrame:',timeBetweenFrame)
print('Before copy animation from crate.msh, typeAnimation :',typeAnimation)
if tMyMeshDebug:copyAnimationsFromMesh(tMesh) then
animation,initialFrame,finalFrame, timeBetweenFrame, typeAnimation = tMyMeshDebug:getAnim(1)
print('green','Now meshDebug has the same animation details as tMesh')
print('Before copy animation from crate.msh, animation :',animation)
print('After copy animation from crate.msh, initialFrame :',initialFrame)
print('After copy animation from crate.msh, finalFrame :',finalFrame)
print('After copy animation from crate.msh, timeBetweenFrame:',timeBetweenFrame)
print('After copy animation from crate.msh, typeAnimation :',typeAnimation)
end
end
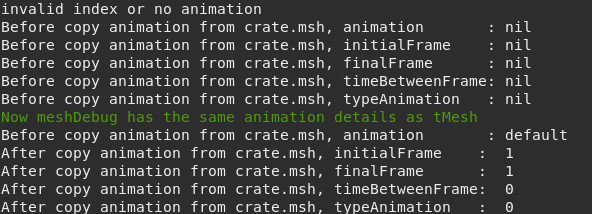
Figure 9.3 Possible output.¶
9.3.6. meshDebug mode draw¶
- setModeDraw(string mode)¶
Modify the mode of draw.
- Parameters
string – mode could be one of option from table modeDraw.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('crate.msh') then
print('Mode draw before:', tMesh:getModeDraw())
tMesh:setModeDraw('TRIANGLE_FAN')
print('Mode draw after:', tMesh:getModeDraw())
end
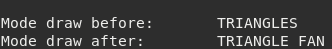
- getModeDraw(string mode)¶
Retrieve the mode of draw.
- Returns
modewill be one of option from table modeDraw.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('crate.msh') then
print('Mode draw before:', tMesh:getModeDraw())
tMesh:setModeDraw('TRIANGLE_FAN')
print('Mode draw after:', tMesh:getModeDraw())
end

Figure 9.4 mode draw¶
9.3.7. meshDebug Cull face¶
- setModeCullFace(string mode)¶
Modify the mode cullFace face.
- Parameters
string – mode could be one of option from table cullFace.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('crate.msh') then
print('Mode cull face before:', tMesh:getModeCullFace())
tMesh:setModeCullFace('BACK')
print('Mode cull face after:', tMesh:getModeCullFace())
end
- getModeCullFace(string mode)¶
Modify the mode cullFace face.
- Returns
modewill be one of option from table cullFace.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('crate.msh') then
print('Mode cull face before:', tMesh:getModeCullFace())
tMesh:setModeCullFace('BACK')
print('Mode cull face after:', tMesh:getModeCullFace())
end
9.3.8. meshDebug front face¶
- setModeFrontFace(string mode)¶
Modify the mode front face.
- Parameters
string – mode could be one of option from table front face.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('crate.msh') then
print('Mode front face before:', tMesh:getModeFrontFace())
tMesh:setModeFrontFace('CW')
print('Mode front face after:', tMesh:getModeFrontFace())
end
- getModeFrontFace(string mode)¶
Retrieve the mode front face.
- Returns
modewill be one of option from table front face.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('crate.msh') then
print('Mode front face before:', tMesh:getModeFrontFace())
tMesh:setModeFrontFace('CW')
print('Mode front face after:', tMesh:getModeFrontFace())
end
9.3.9. meshDebug frame¶
- getTotalFrame¶
Retrieve the total frame of mesh.
- Returns
numbertotal of frame.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('crate.msh') then
local total_frame = tMesh:getTotalFrame()
print('the mesh has ' , total_frame, ' frames')
end
9.3.10. meshDebug subset¶
- getTotalSubset(number frame)¶
Retrieve the total subset given a frame.
- Parameters
number – frame .
- Returns
numbertotal of subset in the indicated frame.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('crate.msh') then
local total_subset = tMesh:getTotalSubset(1)
print('the mesh has ' , total_subset, ' subset at frame 1')
end
9.3.11. meshDebug vertex¶
- addVertex(number frame, number subset)¶
Add a single vertex given frame and subset.
- Parameters
number – frame
number – subset
- Returns
booleanresult of operation.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
local result = tMesh:addVertex(1,1)
- addVertex(number frame, number subset, number total_vertex)¶
Add vertex given frame, subset and the total of vertex.
- Parameters
number – frame
number – subset
number – total vertex to be added
- Returns
booleanresult of operation.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
local total_vertex = 5
local result = tMesh:addVertex(1,1,total_vertex)
- addVertex(number frame, number subset, table vertex)¶
Add a vertex given frame, subset and the vertex itself in a table.
- Parameters
number – frame
number – subset
table – vertex to be added
{x,y,z,nx,ny,nz,u,v}
- Returns
booleanresult of operation.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
local vertex = {x = 0,y = 10,z = 1,nx = 0,ny = 0 ,nz = 1,u = 0 ,v = 1}
local result = tMesh:addVertex(1,1,vertex)
- addVertex(number frame, number subset, table vertex_array)¶
Add an array of vertex given frame, subset and the vertex array in a table.
- Parameters
number – frame
number – subset
table – vertex array to be added
{{x,y,z,nx,ny,nz,u,v},{x,y,z,nx,ny,nz,u,v}, ...
- Returns
booleanresult of operation.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
local vertex = {{x = 0,y = 10,z = 1,nx = 0,ny = 0 ,nz = 1,u = 0 ,v = 1}, {x = 1,y = 0,z = 1,nx = 0,ny = 0 ,nz = 1,u = 0.5 ,v = 0.5}}
local result = tMesh:addVertex(1,1,vertex)
- getTotalVertex(number frame, number subset)¶
Retrieve the total vertex given frame and subset.
- Parameters
number – frame
number – subset
- Returns
numbertotal of vertex in the indicated frame from subset.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('crate.msh') then
local total_vertex = tMesh:getTotalVertex(1,1)
print('the mesh has ' , total_vertex, ' vertex in the subset (1) at frame (1)')
end
- getVertex(number * index_frame, number * index_subset, number * index_vertex, number * max_vertex_return)¶
Get one or more vertices.
- Parameters
number – index_frame from 1 to max number of frame (use getTotalFrame) (default is 1)
number – index_subset from 1 to max number of subset (use getTotalSubset) (default is 1)
number – index_vertex from 1 to max number of vertex (use getTotalVertex) (default is 1)
number – max_vertex_return from 1 to max number of vertex (use getTotalVertex) (default is 1)
- Returns
single
tableor multiplestablefilled with the vertices.
The Table will have
x,y,zcoordinates,u,vmap to texture andnx,ny,nzrepresenting the normal.Example getting a single vertex:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
local vertex = tMesh:getVertex() -- will retrieve 1 because the default value (1 for total vertex, so one single table)
print('x: ', vertex.x)
print('y: ', vertex.y)
print('z: ', vertex.z)
print('u: ', vertex.u)
print('v: ', vertex.v)
print('nx:', vertex.nx)
print('ny:', vertex.ny)
print('nz:', vertex.nz)
end
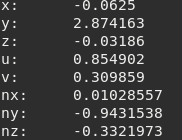
Figure 9.5 Possible output¶
Example getting a specific single vertex:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
local index_frame = 1
local index_subset = 1
local index_vertex = 10 --our specific vertex
local vertex = tMesh:getVertex(index_frame,index_subset,index_vertex)
print('x: ', vertex.x)
print('y: ', vertex.y)
print('z: ', vertex.z)
print('u: ', vertex.u)
print('v: ', vertex.v)
print('nx:', vertex.nx)
print('ny:', vertex.ny)
print('nz:', vertex.nz)
end
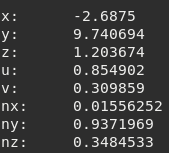
Figure 9.6 Possible output¶
Example getting a designed amount of vertex:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
local index_frame = 1
local index_subset = 1
local index_vertex = 10 --our specific vertex
local total_vertex = 3 -- we want 3 vertices
--(you can get them all , just pass a number very high, like 9E9)
local vertices = tMesh:getVertex(index_frame,index_subset,index_vertex,total_vertex)
for i=1, #vertices do
local vertex = vertices[1]
print('\nVertex number:',i )
print('x: ', vertex.x)
print('y: ', vertex.y)
print('z: ', vertex.z)
print('u: ', vertex.u)
print('v: ', vertex.v)
print('nx:', vertex.nx)
print('ny:', vertex.ny)
print('nz:', vertex.nz)
end
end
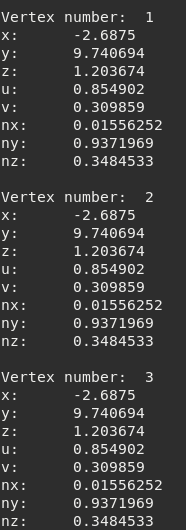
Figure 9.7 Possible output¶
- setVertex(number index_frame, number index_subset, number index_vertex, number max_vertex_return, table vertex)¶
Set one or more vertices.
- Parameters
number – index_frame from 1 to max number of frame (use getTotalFrame)
number – index_subset from 1 to max number of subset (use getTotalSubset)
number – index_vertex from 1 to max number of vertex (use getTotalVertex)
number – max_vertex_return from 1 to max number of vertex (use getTotalVertex)
table – vertex to be set. the table can be unique or array.
The Table could have
x,y,zcoordinates,u,vmap to texture andnx,ny,nzrepresenting the normal. Values not set will not be changed.Example setting a single vertex:
function printVertex(vertex)
print('\n')
print('x: ', vertex.x)
print('y: ', vertex.y)
print('z: ', vertex.z)
print('u: ', vertex.u)
print('v: ', vertex.v)
print('nx:', vertex.nx)
print('ny:', vertex.ny)
print('nz:', vertex.nz)
end
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
local index_frame = 1
local index_subset = 1
local index_vertex = 10 --our specific vertex
local vertex = tMesh:getVertex(index_frame,index_subset,index_vertex)
printVertex(vertex)
vertex.x = 0
vertex.y = 1
vertex.z = 2
vertex.nx = 10
vertex.ny = 11
vertex.nz = 12
vertex.u = nil
vertex.v = nil
--we will not modify u and v
tMesh:setVertex(index_frame,index_subset,index_vertex,vertex)
vertex = tMesh:getVertex(index_frame,index_subset,index_vertex)
printVertex(vertex)
end
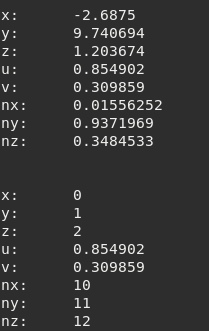
Figure 9.8 Possible output¶
Example setting two vertices:
function printVertex(vertex)
print('\n')
print('x: ', vertex.x)
print('y: ', vertex.y)
print('z: ', vertex.z)
print('u: ', vertex.u)
print('v: ', vertex.v)
print('nx:', vertex.nx)
print('ny:', vertex.ny)
print('nz:', vertex.nz)
end
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
local index_frame = 1
local index_subset = 1
local index_vertex = 10 --our specific vertex
local vertex = tMesh:getVertex(index_frame,index_subset,index_vertex)
printVertex(vertex)
vertex.x = 3
vertex.y = 2
vertex.z = 1
vertex.nx = 1.10
vertex.ny = 1.11
vertex.nz = 1.12
vertex.u = nil
vertex.v = nil
--we will not modify u and v
tVertices = {[1] = vertex, [2] = vertex}--we instruct to change itself and the next one
tMesh:setVertex(index_frame,index_subset,index_vertex,tVertices)
vertex = tMesh:getVertex(index_frame,index_subset,index_vertex + 1)-- we will get the next vertex
printVertex(vertex)
end
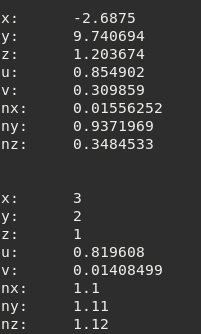
Figure 9.9 Possible output¶
9.3.12. meshDebug index buffer¶
- getTotalIndex(number frame, number subset)¶
Retrieve the total index buffer given frame and subset.
- Parameters
number – frame
number – subset
- Returns
numbertotal of index buffer in the indicated frame from subset.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('crate.msh') then
local index_buffer = tMesh:getTotalIndex(1,1)
print('the mesh has ' , index_buffer, ' index buffer in the subset (1) at frame (1)')
end
- isIndexBuffer¶
Verify if is indexed buffer.
- Returns
booleanresult indicating if is indexed buffer.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('crate.msh') then
local bIndexed = tMesh:isIndexBuffer()
print('the mesh is indexed buffer:' , tostring(bIndexed))
end
- getIndex(number frame, number subset)¶
Retrieve a index buffer given frame and subset.
- Parameters
number – frame
number – subset
- Returns
tableresult of operation.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
local index_frame = 1
local index_subset = 1
local indexBuffer = tMesh:getIndex(index_frame,index_subset)
if indexBuffer then --has index buffer
for i = 1, #indexBuffer do
print(indexBuffer[i])
end
else
print('Object hs no index buffer!')
end
end
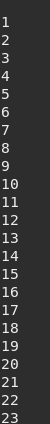
Figure 9.10 Dummy index buffer¶
- addIndex(number frame, number subset, table index_array)¶
Add index buffer given frame and subset.
- Parameters
number – frame
number – subset
table – index array (one based)
- Returns
booleanresult of operation.
Follow an example how to add index buffer and how to save a mesh to a binary file:
1 mbm.setColor(1,1,1) --set background color to white 2 3 function createCubeFace() 4 5 local tCube = { {x=-50,y=-50,z=0}, 6 {x=-50,y=50,z=0}, 7 {x=50,y=-50,z=0}, 8 {x=50,y=50,z=0}} 9 local tIndex = {1,2,3, 3,2,4} 10 local sTextureFileName = 'crate.png' 11 12 return tCube, tIndex, sTextureFileName 13 end 14 15 function saveMeshToBinaryFile(fileName,tVertex,tIndex,sTexture) 16 17 --meshDebug is used to create dynamically mesh in the engine. 18 --For mesh it has to have at least one frame to be able to generate the mesh 19 local stride = 3 --stride only can be 3 or 2. it means (x,y,z) or (x,y) 20 local tMesh = meshDebug:new() --new mesh debug to store the information about our mesh 21 local nFrame = tMesh:addFrame(stride) -- Add one frame with stride 3 (x,y,z) 22 local indexFrame = nFrame --(meshDebug uses 1 based index) 23 local indexSubset = 1 --first subset (1 based index) 24 25 26 --To add vertex, first we need to add a subset 27 local nSubset = tMesh:addSubSet(indexFrame) --add one subset for the first frame 28 29 --we are adding vertex to frame (next) 30 --this vertex list has to have at least 3 vertex (one triangle) to be valid 31 -- The table expected is : {{x,y,z},{x,y,z},{x,y,z}, ...} 32 if not tMesh:addVertex(indexFrame,indexSubset,tVertex) then 33 print("Error on add vertex buffer") 34 return false 35 end 36 37 if not tMesh:addIndex(indexFrame,indexSubset,tIndex) then 38 print("Error on add index buffer") 39 return false 40 end 41 42 --apply the texture to frame / subset 43 if not tMesh:setTexture(indexFrame,indexSubset,sTexture) then 44 print("Error on set texture!") 45 return false 46 end 47 48 tMesh:setType('mesh') -- set it to mesh type 49 50 local calcNormal,calcUv = true,true --Instruct to calculate normal and UV 51 if tMesh:save(fileName,calcNormal,calcUv) then 52 print("Mesh created successfully ") 53 return true 54 else 55 print("Failed to create Mesh!") 56 return false 57 end 58 59 end 60 61 62 function onInitScene() 63 64 tMesh = mesh:new('3D')-- our object which will load from binary file 65 66 local sFileNameMesh = 'crate.msh' 67 68 local tCubeVertex, tCubeIndex, sCubeTextureFileName = createCubeFace()--create our cube face 69 70 if saveMeshToBinaryFile(sFileNameMesh,tCubeVertex, tCubeIndex, sCubeTextureFileName) then 71 tMesh:load(sFileNameMesh) --all coordinate already in place 72 else 73 print('Failed to create ' .. sFileNameMesh) 74 mbm.quit() 75 end 76 77 78 --set up camera 79 camera3d = mbm.getCamera('3D') 80 camera3d:setPos(0,0,-500) 81 camera3d:setFocus(0,0,0) 82 83 --need to rotate our object 84 tMouse = {x=0,y=0,clicked = false} 85 end 86 87 function onTouchDown(key,x,y) 88 tMouse.clicked = true 89 tMouse.x = x 90 tMouse.y = y 91 end 92 93 function onTouchMove(key,x,y) 94 if tMouse.clicked then 95 local diff_X = tMouse.x - x 96 local diff_Y = tMouse.y - y 97 tMouse.x = x 98 tMouse.y = y 99 100 --simple rotation based on mouse 101 tMesh.ay = tMesh.ay + math.rad(diff_X) 102 tMesh.ax = tMesh.ax + math.rad(diff_Y) 103 104 end 105 end 106 107 function onTouchUp(key,x,y) 108 tMouse.clicked = false 109 end
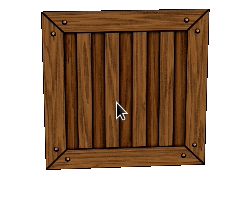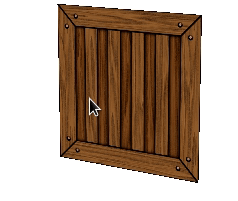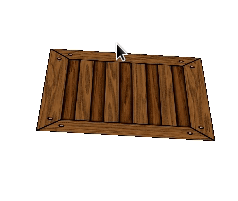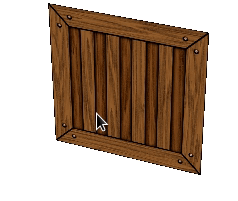
Figure 9.11 Adding index buffer¶
9.3.13. meshDebug texture¶
- getTexture(number frame, number subset)¶
Get the current texture name given frame and subset.
- Parameters
number – frame
number – subset
- Returns
string-file namefrom texture.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
local index_frame = 1
local index_subset = 1
local texture = tMesh:getTexture(index_frame,index_subset)
if texture then --has texture
print('texture:',texture)
else
print('Object has no texture!')
end
end

Figure 9.12 Get the texture name from meshDebug¶
- setTexture(number frame, number subset, string texture)¶
Set a new texture given frame, subset and texture name.
- Parameters
number – frame
number – subset
string – texture name or
nilto unset.
- Returns
boolean-resultfrom meshDebug.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
local index_frame = 1
local index_subset = 1
local texture = 'mike.png'
print('texture name current:',tMesh:getTexture(index_frame,index_subset))
local bSuccess = tMesh:setTexture(index_frame,index_subset,texture)
if bSuccess then
print('texture changed successfully:',tMesh:getTexture(index_frame,index_subset))
else
print('Failed to set the new texture!')
end
end
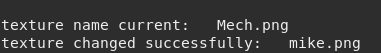
Figure 9.13 Setting texture to meshDebug¶
Note
Note that meshDebug will not check if the texture exists or not!
9.3.14. meshDebug stride¶
- setStride(number stride, number * frame)¶
Set a specific stride to specific frame or all frames.
- Parameters
number – stride 2
x, yor 3x, y, znumber – frame 0 for all frames or specific frame one based index.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
local stride = 3 -- x,y,z
local frame = 0
tMesh:setStride(stride,frame)
end
9.3.15. meshDebug normal¶
- enableNormal(boolean enable)¶
Enable or disable normal to be saved in the mesh
- Parameters
boolean – value
trueorfalse
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
tMesh:enableNormal(true)
end
9.3.16. meshDebug UV¶
- enableUv(boolean enable)¶
Enable or disable uv to be saved in the mesh
- Parameters
boolean – value
trueorfalse
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
tMesh:enableUv(true)
end
9.3.17. meshDebug Physics¶
- getPhysics¶
Return an array of physics.
- Returns
table- Physics.
Example:
function printTable(space, tTbale)
for k, v in pairs(tTbale) do
if k == 'type' then
-- Do nothing ... we already have printed type
elseif type(v) == 'table' then
if string.len(space) > 0 then
print(space,k,v)
else
print(k,v)
end
printTable(space .. '\t', v)
else
if string.len(space) > 0 then
print(space, k, v)
else
print(k, v)
end
end
end
end
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
local tPhysics = tMesh:getPhysics()
for i =1 , #tPhysics do
local tPhysic = tPhysics[i]
print('physic index[' .. tostring(i) .. '] type:',tPhysic.type)
printTable('', tPhysic)
end
end
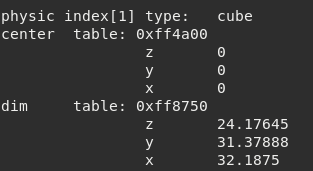
Figure 9.14 Possible output for get physics¶
- setPhysics(table tPhysics)¶
Set physics from a table.
- Parameters
table – of physics.
The following table describe how should be the table of physics:
type /namesub tableinformationvaluesinformationcubecenterdimx, y, zx, y, ztriangleabcx, y, zx, y, zx, y, zspherecenterrayx, y, zcomplexabcdefghx, y, zx, y, zx, y, zx, y, zx, y, zx, y, zx, y, zx, y, zExample setting complex table physic:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
local tComplex = { type = 'complex',
a = {x = 1, y = 1, z = 1},
b = {x = 2, y = 2, z = 2},
c = {x = 3, y = 3, z = 3},
d = {x = 4, y = 4, z = 4},
e = {x = 5, y = 5, z = 5},
f = {x = 6, y = 6, z = 6},
g = {x = 7, y = 7, z = 7},
h = {x = 8, y = 8, z = 8}}
tMesh:setPhysics(tComplex)
local tPhysics = tMesh:getPhysics()
local tPhysic = tPhysics[1]
print(tPhysic.type)
print('a',tPhysic.a.x,tPhysic.a.y,tPhysic.a.z)
print('b',tPhysic.b.x,tPhysic.b.y,tPhysic.b.z)
print('c',tPhysic.c.x,tPhysic.c.y,tPhysic.c.z)
print('d',tPhysic.d.x,tPhysic.d.y,tPhysic.d.z)
print('e',tPhysic.e.x,tPhysic.e.y,tPhysic.e.z)
print('f',tPhysic.f.x,tPhysic.f.y,tPhysic.f.z)
print('g',tPhysic.g.x,tPhysic.g.y,tPhysic.g.z)
print('h',tPhysic.h.x,tPhysic.h.y,tPhysic.h.z)
end
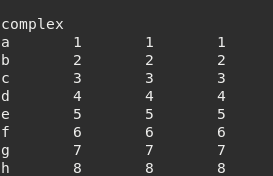
Figure 9.15 Output for complex table physic¶
Example setting multiple table physics:
function createTableCubePhysics()
local tCube = { type = 'cube',
center = {x = 0.1, y = 0.2, z = 0.3},
half = {x = 5.0, y = 6.0, z = 7.0}}
return tCube
end
function createTableTrianglePhysics()
local tTriangle = { type = 'triangle',
a = {x = -1, y = -1, z = 0.1},
b = {x = 1, y = 1, z = 0.1},
c = {x = 1, y = -1, z = 0.1}}
return tTriangle
end
function createTableSpherePhysics()
local tSphere = { type = 'sphere',
center = {x = -0.3, y = -0.1, z = 0.1},
ray = 5.56}
return tSphere
end
function createTableComplexPhysics()
local tComplex = { type = 'complex',
a = {x = 1, y = 1, z = 1},
b = {x = 2, y = 2, z = 2},
c = {x = 3, y = 3, z = 3},
d = {x = 4, y = 4, z = 4},
e = {x = 5, y = 5, z = 5},
f = {x = 6, y = 6, z = 6},
g = {x = 7, y = 7, z = 7},
h = {x = 8, y = 8, z = 8}}
return tComplex
end
function printPhysics(tMesh)
local tPhysics = tMesh:getPhysics()
print('Total physics:',#tPhysics)
for i=1, #tPhysics do
local tPhysic = tPhysics[i]
print('\n')
print('type:',tPhysic.type)
if tPhysic.type == 'cube' then
print('center',tPhysic.center.x,tPhysic.center.y,tPhysic.center.z)
print('half',tPhysic.half.x,tPhysic.half.y,tPhysic.half.z)
elseif tPhysic.type == 'triangle' then
print('a',tPhysic.a.x,tPhysic.a.y,tPhysic.a.z)
print('b',tPhysic.b.x,tPhysic.b.y,tPhysic.b.z)
print('c',tPhysic.c.x,tPhysic.c.y,tPhysic.c.z)
elseif tPhysic.type == 'sphere' then
print('center',tPhysic.center.x,tPhysic.center.y,tPhysic.center.z)
print('ray',tPhysic.ray)
elseif tPhysic.type == 'complex' then
print('a',tPhysic.a.x,tPhysic.a.y,tPhysic.a.z)
print('b',tPhysic.b.x,tPhysic.b.y,tPhysic.b.z)
print('c',tPhysic.c.x,tPhysic.c.y,tPhysic.c.z)
print('d',tPhysic.d.x,tPhysic.d.y,tPhysic.d.z)
print('e',tPhysic.e.x,tPhysic.e.y,tPhysic.e.z)
print('f',tPhysic.f.x,tPhysic.f.y,tPhysic.f.z)
print('g',tPhysic.g.x,tPhysic.g.y,tPhysic.g.z)
print('h',tPhysic.h.x,tPhysic.h.y,tPhysic.h.z)
else
print('ERR','type physics unknown')
end
end
end
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('Mech.msh') then
local tCube = createTableCubePhysics()
local tTriangle = createTableTrianglePhysics()
local tSphere = createTableSpherePhysics()
local tComplex = createTableComplexPhysics()
local tPhysics = { [1] = tSphere, [2] = tCube, [3] = tComplex, [4] = tTriangle }
tMesh:setPhysics(tPhysics)
printPhysics(tMesh)
end
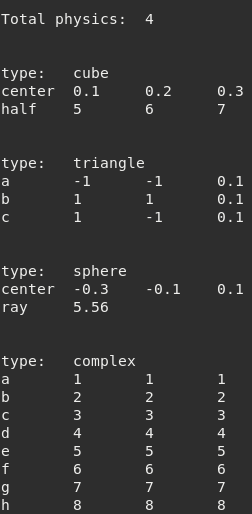
Figure 9.16 Output for multiples physic¶
9.3.18. meshDebug centralize¶
- centralize(number * frame, number * subset)¶
Centralize a specific frame/subset or all of them (do not supply the arguments)
- Parameters
number – frame from 1 to total of frames.
number – subset from 1 to total of subset.
Example:
tMesh = meshDebug:new()
if tMesh:load('crate.msh') then
tMesh:centralize() -- centralize all of them
end